It is estimated that, in 2017, liver cancer will be the fifth leading cause of cancer death in men and the eighth leading cause of cancer deaths in women in the U.S. When cancer spreads to the liver from another part of the body it is not considered liver cancer, and is still named after the part of the body where it originated. So, when lung cancer metastasizes to the liver, it does not become “liver cancer”, it is still lung cancer.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer
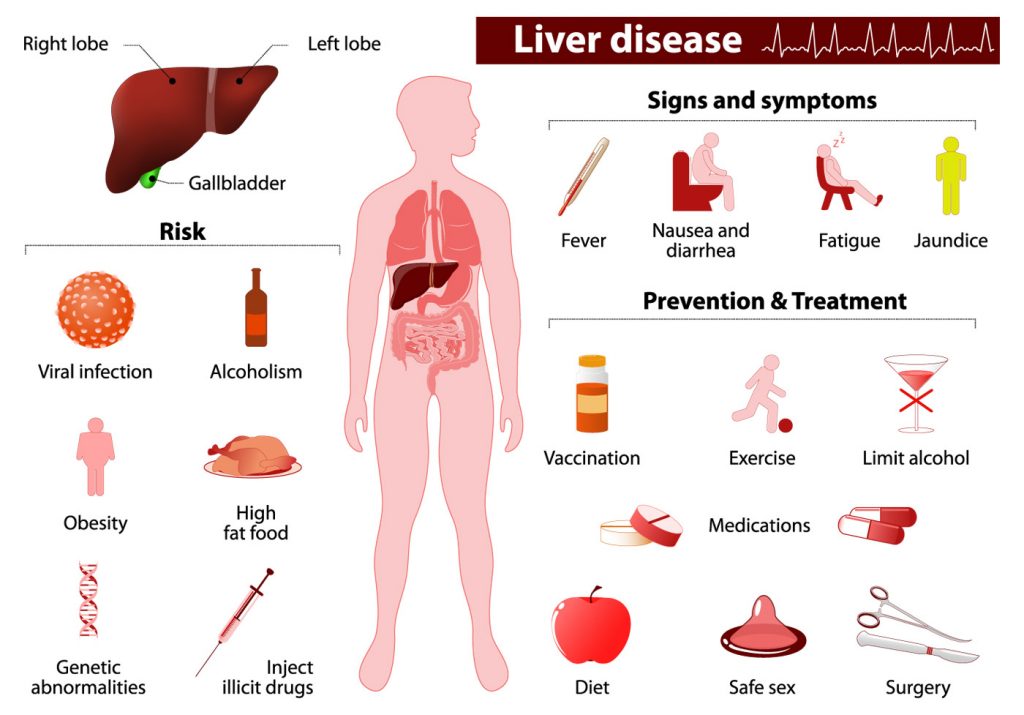
In most people, liver cancer doesn’t cause symptoms until later stages, but some symptoms appear earlier. Early detection is important in any type of cancer and liver cancer is no exception. If you experience any of these symptoms of liver cancer, talk to your doctor right away:
- Pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen, on the right side
- Pain in your right shoulder blade or in your back
- Yellowing of the skin and/or whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Abdominal swelling
- Hard lump on your right side just below your ribcage
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- White, chalky stools
Liver Cancer Causes and Risk Factors
The cause of liver cancer is not always known. Factors that increase your risk of developing include:
- Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV).
- Chronic infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV).
- Certain inherited liver diseases including Wilson’s disease and hemochromatosis.
- Exposure to aflatoxins which are poisons produced by molds that grow on certain foods, such as peanuts and corn, when they are not stored properly. Aflatoxin contamination is not common in the U.S., and is more common in certain parts of Asia and Africa.
- Exposure to tricholoroethylene (TCE). TCE is a solvent, often used for cleaning or degreasing. It used to be used in dry cleaning.
- Cirrhosis, a condition which causes scar tissue to form in the liver.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Diabetes.
- Obesity.
- Heavy alcohol use.
