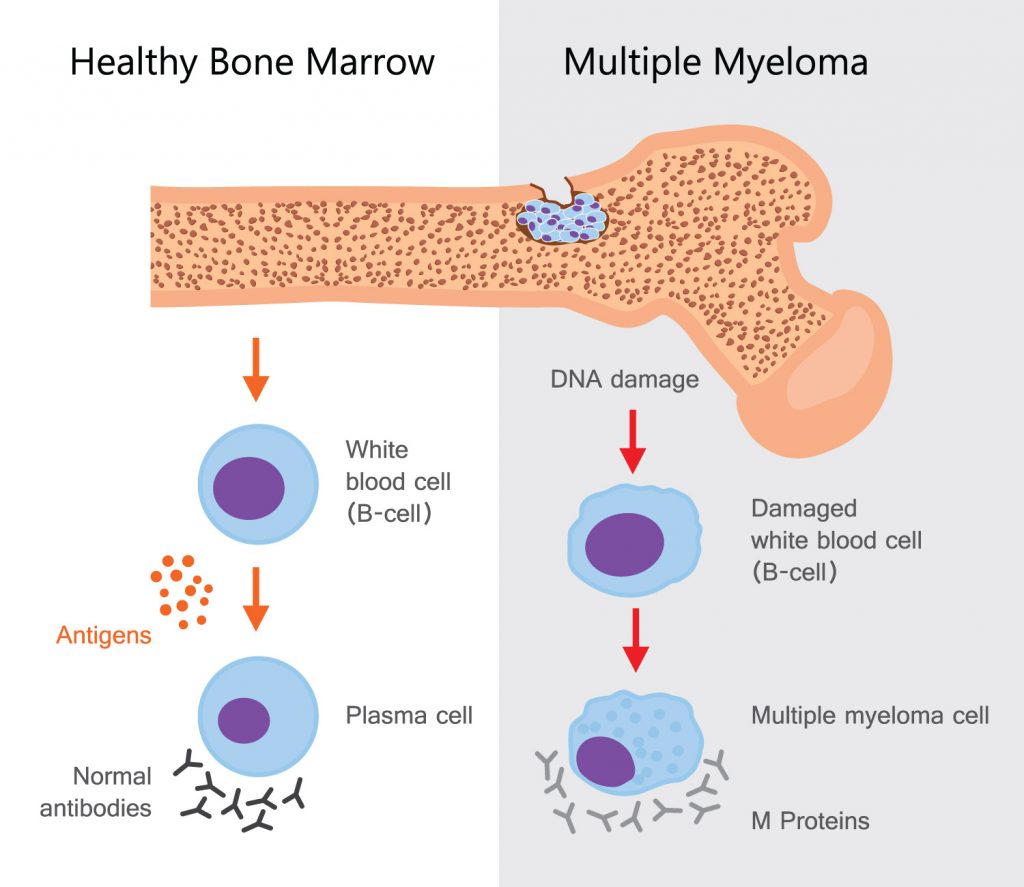
Multiple myeloma is a type of blood cancer. Blood cancer is also referred to as hematological cancer. Multiple myeloma develops in plasma cells found in the bone marrow. Plasma cells are a type of white blood cells, an important part of your immune system. As such, people with multiple myeloma may experience frequent infections, as well as other health problems. Multiple myeloma often responds well to treatment and in patients who are not experiencing symptoms doctors may recommend delaying treatment. However, early treatment is still best so that you and your doctor can determine the best course of action for you.
Multiple Myeloma Symptoms
Symptoms of multiple myeloma can include:
- Bone pain, often in the spine or chest
- Bone fractures
- Increased or decreased urination
- Increased thirst
- Impaired kidney function
- Fatigue
- Restlessness followed by fatigue and weakness
- Confusion
- Brain fog
- Frequent infections
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Weakness or numbness in the legs
- Breathlessness
- Easy bruising or bleeding
Complications of multiple myeloma can include:
- Low red blood cell count
- Problems with the bones
- Frequent infections
- Kidney problems
Multiple Myeloma Risk Factors
The cause of multiple myeloma is not known. Although there is an increased risk with a family history, it is not considered and inherited disease. There are many factors associated with an increased risk of developing multiple myeloma including:
- Being over 60
- Being male
- Being black
- Family history of multiple myeloma
- Having HIV or AIDS
- Having certain autoimmune disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis
- Having monoclonal gammopathy (MGUS)
- Exposure to certain toxin including benzene, asbestos, heavy metals, herbicides, insecticides and petroleum products
- Radiation exposure
- Obesity
