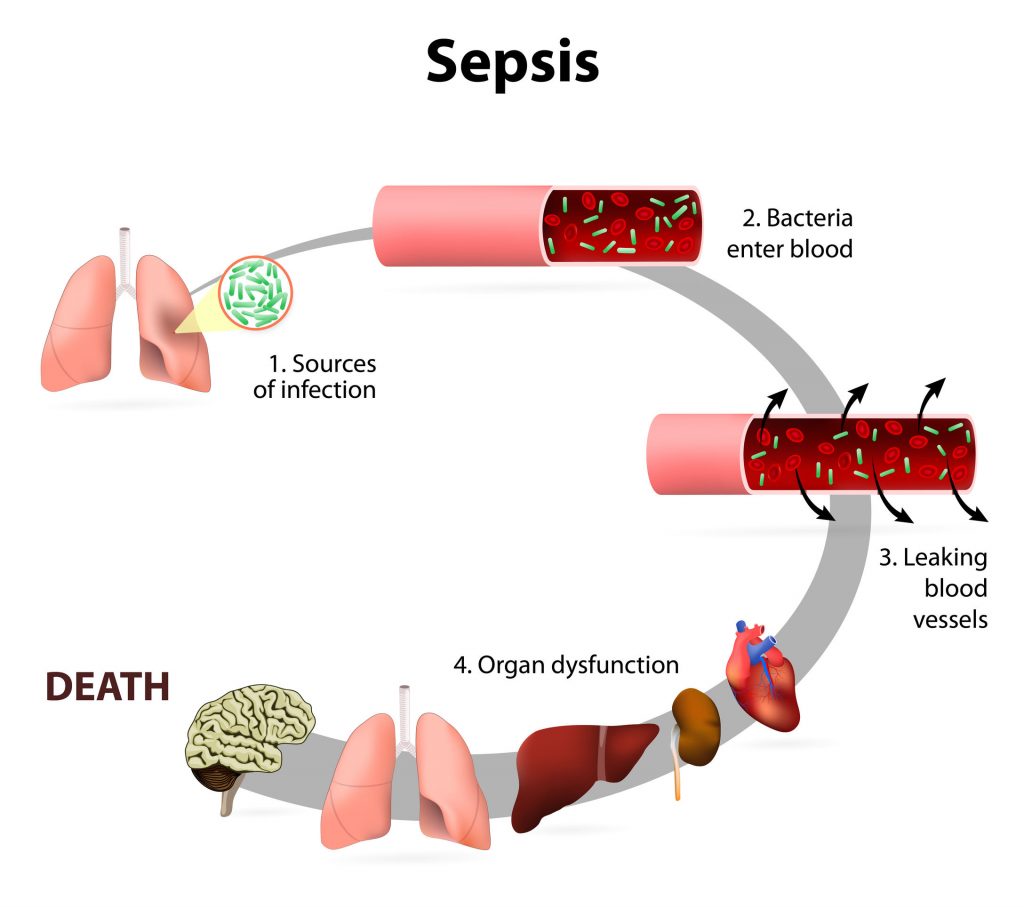
Sepsis is a reaction to infection that can ultimately lead to multiple organ failure and death. Sepsis is not the infection itself, but an immune response gone wild. It is sometimes confused with septicemia, which is an infection and one that can lead to sepsis. The symptoms of sepsis can mimic the symptoms of infection. Early treatment improves the chance of survival. As sepsis progresses to more serious stages it is referred to as severe sepsis and septic shock.
Causes of Sepsis
Sepsis is caused by infection. It happens when your immune system releases chemicals into your bloodstream that cause inflammation throughout your whole body. Any type of infection has the potential to lead to sepsis. This includes bacterial, viral, and fungal infections of all types. Those which most commonly lead to sepsis include:
- “Blood poisoning” technically called septicemia or bacteremia
- Pneumonia
- Kidney infection
- Abdominal infection
- Urinary tract infection
- Skin infection
Anyone can develop sepsis. People with weakened immune system and the elderly are at greatest risk.
Symptoms of Sepsis
Without treatment, sepsis is fatal. Even with treatment, it is often fatal. The earlier it is treated, the more likely that treatment will be life-saving. If you have or have recently had an infection, and experience any of the following symptoms, seek immediate medical attention or call and ambulance and let them know about the infection:
- Fever
- Rapid heart rate
- Rapid breathing
- Heavy sweating
- Unusually low urine output
- Slurred speech
- Diarrhea
- Nausea or vomiting
- Severe muscle pain
- Confusion
- Unusual change in mental state
- A feeling of impending doom
- Dizziness
- Feeling faint
- Skin that is unusually cold or unusually warm
- Skin that is pale, discolored or mottled
- Skin that is cool and pale at the extremities
- Loss of consciousness
