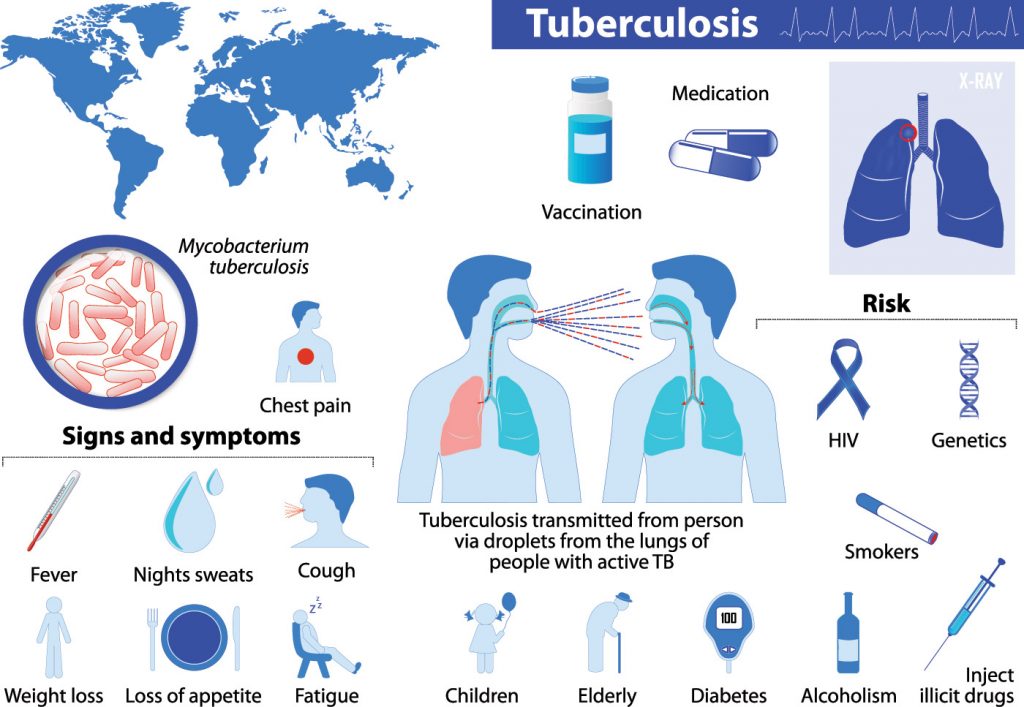
If you’re like most people, you think of tuberculosis as a famous disease from history, not something we have to worry about today. Also known as “consumption”, tuberculosis was a notorious killer in the 18th and 19th centuries. In 1882, Robert Koch discovered the cause of TB, paving the way for vaccines and treatments. It was predicted that TB would be eradicated by 2025. But that did not come to pass and it is now the leading cause of death from infectious disease worldwide.
What is Tuberculosis?
TB is a bacterial infection, usually of the lungs. Symptoms include:
- Coughing, with or without mucus or blood
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Chills
- Night sweats
Tuberculosis is fatal in about two-thirds of people who do not get proper treatment.
Latent VS Active Tuberculosis
In latent TB, the bacteria are in your body, just hanging out waiting to activate. You don’t have symptoms and you are not contagious. However, latent TB can become active. It is more likely to become active in people with compromised immune systems.
Active TB causes symptoms and is contagious. However, it is usually not contagious in people who have been in treatment for at least two weeks.
Treating Tuberculosis
Both latent and active TB are treated with antibiotics. Treatment typically lasts about six months, and the medications can be toxic. The number and types of mediations needed will depend on factors including whether it is latent or active and whether it is multidrug resistant TB. Completing the course of treatment, even if symptoms have subsided, is necessary to preventing the bacteria from becoming drug resistant.
